CPCA Training and Certification Process
Do you need petroleum mechanic certification? Certification to work on petroleum systems is required in most jurisdictions across Canada, including Federal Land. The CPCA certification program combines theoretical training, exams, and on-the-job practical experience working with a petroleum mechanic holding the appropriate license. The hours of practical experience vary for each license (1000 hours for PM1, 2000 hours for PM2, and 500 hours for PM3). Once an individual completes all the requirements for certification, they can apply to CPCA for their license.
CPCA’s training and certification program was developed to provide a national training standard for individuals entering the petroleum mechanic industry and for experienced technicians. The program is based on national standards, including the National Fire Code and the Canadian Council Ministers of the Environment—Code of Practices.
Our courses are a self-study, modular format and are delivered by the CPCA with the support of our member provincial associations.
The Path to Certification
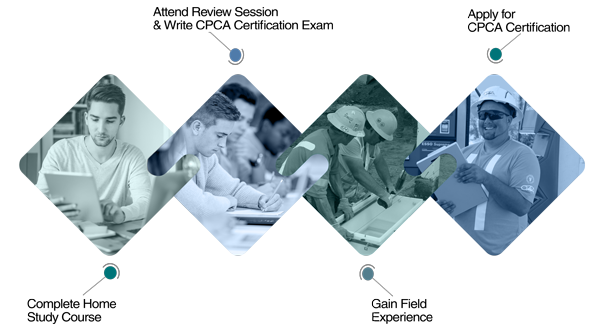
Home Study Program
CPCA training utilizes a blended learning method combining home study material with online tools and in-class review sessions with qualified instructors. The home study course is self-led; students can study the material on their own time with each course taking an average of forty hours to complete. Students also have access to our online learning platform with tutorials for tank installation, piping, dispenser maintenance and activities that challenge the student based on what they have learned throughout the course.
The CPCA home study program provides the necessary theoretical training in preparation for the required course examinations. Click on the HOME STUDY page under the training menu for information
Challenge Process
The Challenge Process allows individuals who hold other relevant provincial certifications and have the required practical experience to apply for a Petroleum Mechanic license without participating in theoretical training.
Relevant certification includes ITA BC & Nova Scotia Petroleum Installer certification.
The Challenge process does not replace the traditional method of home study training. If you do not have relevant certification, you must go through the home study training program.
Applicants are to be approved by the CPCA based on sufficient practical experience to be determined by the CPCA. Challenge participants are supplied with a training manual and must complete the appropriate certification exam.
The CPCA Practical Experience Log Book is a helpful tool for determining relevant practical experience. Individuals can refer to the logbook to match the qualifications required for certification.
Applicants may also be required to submit additional material (e.g., employer and/or supervisor letters attesting to the applicant’s work experience and relevant training/manufacturer certification where applicable). The work experience submitted shall match the experience required within the scope of the license application.
Applying for Certification
Once a student has successfully completed their course, exam, and practical skills requirement, they can apply for certification.
Students must submit the following to CPCA as part of their certification application:
- Proof of practical experience (see the Log Book for details)
- Application for Certification (CPCA Form 2)
- Verification of Trade Experience (CPCA Form 3)
- Proof of relevant manufacturer certification (e.g. Dispenser, Piping etc.)
- Employer letter attesting to practical experience completion
Certificate Categories
Below is an overview of the Petroleum Mechanic licenses available. Detailed descriptions are available in the CPCA Policies and Procedures.
PMH – Petroleum Mechanic Helper
A person who holds a PMH license may, without supervision, maintain pumps, including replacing nozzles, spouts, hoses, breakaways, filters, and belts, and may access, contain, and clean up spills and leaks.
The PMH license is a prerequisite to the PM1, PM2 & PM3 certification.
PM1 – Service and Maintenance
A person who holds a PM1 license may, without supervision, service and maintain petroleum equipment and systems, and accessories essential to their operation.
- Install and remove suction pumps and related systems
- Repair and maintain suction pumps and related systems
- Repair and maintain submersible pumps, dispensers and related systems
- Practical Experience hours required: 1000 hours – under the supervision of a PM1 license holder
PM2 – Underground Installation
A person who holds a PM2 license may, without supervision, install, remove, alter, test, service and maintain any type of underground installation and the equipment and accessories essential to its operation.
- Install underground tanks
- Remove underground tanks
- Install petroleum transfer systems
- Repair and maintain systems for detecting leaks and monitoring tanks
- Install and remove submersible pumps
- Practical Experience hours required: 2000 hours – under the supervision of a PM2 license holder
PM3 – Aboveground Installation
A person who holds a PM3 license may, without supervision, install, remove, alter, repair, test, service and maintain any type of aboveground installation and the equipment and accessories essential to its operation.
- Install above-ground tanks
- Remove above-ground tanks
- Repair and maintain systems for detecting leaks and monitoring tanks
- Install, remove, repair and maintain bulk handling equipment
- Practical Experience hours required: 500 hours – under the supervision of a PM3 license holder
